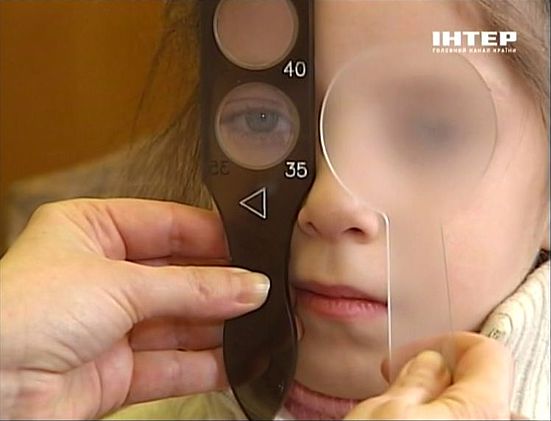
Under certain types and stages of strabismus, patient could be fully recovered. The traditional method of treatment is patching or occlusion, when an opaque bandage is applied to the second normal eye to activate the vision of the squinting eye. It should be combined with a course of special exercises. Treatment of strabismus up to this method requires a lot of time. If within 1.5–2 years the abovesaid measures do not help, other treatment has to be used.
Today in the treatment of strabismus there are two main methods: surgical procedure and therapy by means of special prism glasses.
Prismatic correction as a treatment of strabismus method was applied for a long time, back in the early 50s. For the converging strabismus were used prisms based to the temple, for the with diverging strabismus were used based to the nose (for constant wear). Prisms were prescribed to transfer the image of the squinting eye to the central fossa of the retina (macula) to stimulate the integration of images of both eyes. However, this type of strabismus treatment is not widespread, since it is almost impossible to use ophthalmic prisms, usually glass, with a force of more than 8-10 prism diopters, because of the large weight and dimensions of such prisms.